In the world of investing, choosing the right funds is crucial for achieving your financial goals. Two popular options that often come under consideration are the Vanguard S&P 500 ETF (VOO) and the Vanguard 500 Index Fund Admiral Shares (VFIAX). Both offer exposure to the S&P 500 index, but they have some differences that investors need to understand before making a decision.
Understanding the S&P 500 Index
The S&P 500 is a market-capitalization-weighted index that includes 500 of the largest publicly traded companies in the United States. It represents a broad cross-section of the economy, spanning various sectors such as technology, healthcare, finance, consumer goods, and industrials. Some of the well-known companies in the index include Apple, Microsoft, Amazon, Berkshire Hathaway, and Johnson & Johnson. The index has a long history of providing returns and is often used as a benchmark for the overall performance of the US stock market. Over the long term, it has generally trended upwards, although it has experienced significant short-term fluctuations during market downturns and periods of economic uncertainty.
Vanguard S&P 500 ETF (VOO)
VOO is an exchange-traded fund that aims to track the performance of the S&P 500 index. It offers investors a convenient way to gain exposure to the index in a single trade. Here are some of the key characteristics and advantages of VOO:
Liquidity: ETFs like VOO are highly liquid, meaning they can be easily bought and sold on stock exchanges throughout the trading day. The trading volume of VOO is typically high, which ensures that investors can enter or exit their positions at market prices with relatively low bid-ask spreads. This liquidity makes it a suitable choice for investors who may need to access their funds quickly or who want to engage in short-term trading strategies, although it’s important to note that short-term trading in ETFs still carries risks and may not be suitable for all investors.
Intraday Trading: The ability to trade VOO intraday allows investors to take advantage of short-term price movements. For example, if there is a sudden market event that causes the S&P 500 to fluctuate, an investor can respond quickly by buying or selling VOO shares. However, this also requires a certain level of market knowledge and the ability to monitor the market closely during trading hours.
Cost Structure: VOO has a relatively low expense ratio. The expense ratio represents the annual fee that the fund charges investors to cover its operating costs. A low expense ratio is beneficial as it means more of the investment returns are retained by the investor. For VOO, the expense ratio is typically competitive with other similar ETFs, making it an attractive option for cost-conscious investors.
Transparency: ETFs disclose their holdings on a daily basis, which provides investors with transparency into the underlying assets. In the case of VOO, investors can easily see which stocks are held in the fund and in what proportions. This transparency allows investors to have a clear understanding of the exposure they are getting to different sectors and companies within the S&P 500.
Vanguard 500 Index Fund Admiral Shares (VFIAX)
VFIAX is a mutual fund that also seeks to replicate the performance of the S&P 500 index. It has been a popular choice among investors for many years. Here are some of the features and benefits of VFIAX:
Diversification: By investing in VFIAX, investors gain exposure to the 500 companies in the S&P 500 index, providing a high level of diversification. Diversification helps reduce the risk associated with investing in individual stocks. For example, if one company in the index underperforms due to company-specific issues, the impact on the overall performance of the fund is likely to be mitigated by the performance of the other 499 companies. This diversification is one of the key reasons why index funds like VFIAX are popular among long-term investors.
Long-Term Investment: VFIAX is well-suited for long-term investors who are looking to build wealth over time. The S&P 500 has historically provided solid returns over the long term, and by investing in VFIAX, investors can participate in this growth. The fund’s management team focuses on closely tracking the index, which means that investors can expect the performance of the fund to closely mirror that of the S&P 500 over the long haul. This makes it a reliable option for investors with a time horizon of several years or more, such as those saving for retirement.
Professional Management: Although VFIAX is a passive index fund, it is managed by Vanguard’s team of professionals. The management team is responsible for ensuring that the fund’s holdings accurately reflect the composition of the S&P 500 index. They also handle administrative tasks such as record-keeping, shareholder services, and compliance with regulatory requirements. This professional management provides investors with peace of mind, knowing that their investment is being handled by experienced professionals.
Lower Minimum Investment (for Admiral Shares): VFIAX offers Admiral Shares, which typically have a lower minimum investment requirement compared to some other Vanguard funds. This makes it accessible to a wider range of investors, including those who may be just starting to build their investment portfolios. The lower minimum investment allows investors to get started with a relatively small amount of money and gradually increase their investment over time.
Differences in Structure and Trading
One of the main differences between VOO and VFIAX is their structure. VOO is an ETF, which means it trades on an exchange like a stock. Investors buy and sell VOO shares through a brokerage account, and the price of the ETF fluctuates throughout the trading day based on supply and demand. On the other hand, VFIAX is a mutual fund, and investors typically buy and sell shares directly from the fund company. Mutual funds are priced at the end of each trading day based on the net asset value (NAV) of the fund’s holdings.
This difference in trading and pricing can have implications for investors. For example, if an investor wants to place a market order to buy or sell VOO, they will execute the trade at the current market price, which may be different from the NAV of the underlying index. In contrast, when buying or selling VFIAX, the investor will receive or pay the NAV price calculated at the end of the trading day. Additionally, the trading process for ETFs like VOO may involve additional considerations such as bid-ask spreads and the potential for trading halts or disruptions during periods of high market volatility.
Performance Comparison
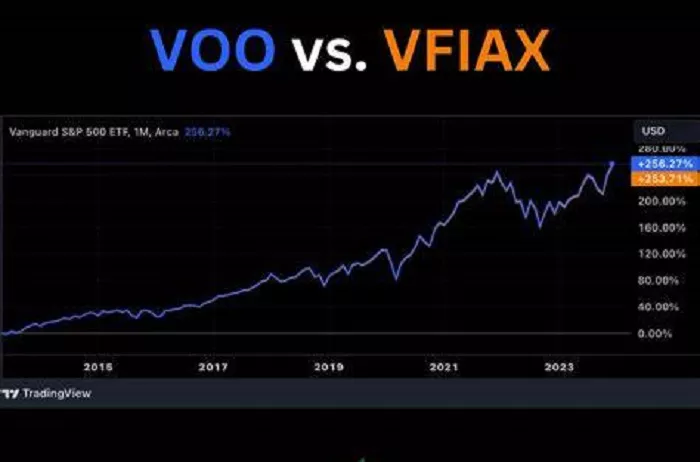
When comparing the performance of VOO and VFIAX, it’s important to note that both funds are designed to track the S&P 500 index. Over the long term, their performance is likely to be very similar, as they are both aiming to replicate the returns of the same index. However, in the short term, there may be some differences due to factors such as tracking error and the impact of trading costs.
Tracking error refers to the degree to which a fund’s performance deviates from the performance of the index it is tracking. Both VOO and VFIAX strive to minimize tracking error, but in practice, there may be slight differences. These differences can be caused by factors such as the fund’s investment strategy, the timing of trades to replicate the index, and the costs associated with managing the fund. For example, if VOO experiences a larger bid-ask spread during a particular trading day, it could slightly impact its performance compared to VFIAX.
It’s also important to consider the impact of fees on performance. While both funds have relatively low expense ratios, even small differences in fees can add up over time and have an impact on the overall returns. For example, if VOO has a slightly lower expense ratio than VFIAX, over a period of many years, the difference in fees could result in a slightly higher cumulative return for investors in VOO. However, it’s important to note that the performance difference due to fees is likely to be relatively small compared to the overall performance of the S&P 500 index.
Tax Considerations
Tax implications are an important aspect of investing. ETFs like VOO are generally considered to be more tax-efficient than some mutual funds. This is because ETFs have a unique structure that allows for in-kind creations and redemptions, which can help minimize the realization of capital gains. When an ETF needs to adjust its holdings to match the index, it can do so through in-kind transactions, which can defer the recognition of capital gains. In contrast, mutual funds like VFIAX may be required to sell securities within the fund to meet redemptions or rebalance the portfolio, which can trigger capital gains distributions to shareholders. These capital gains distributions are taxable to investors, even if they did not sell their shares.
However, it’s important to note that the tax efficiency of both VOO and VFIAX can be influenced by various factors, such as the investor’s holding period, the turnover rate of the fund, and the overall market conditions. For example, if an investor holds VFIAX for a long period and the fund has a relatively low turnover rate, the impact of capital gains distributions may be minimized. Additionally, tax laws and regulations can change over time, which could affect the tax treatment of both funds.
Investor Suitability
The choice between VOO and VFIAX depends on several factors related to the investor’s individual circumstances and investment goals.
Investment Horizon: For investors with a short-term investment horizon, such as those who may need to access their funds within the next few years, VOO’s liquidity and intraday trading capabilities may be more appealing. However, it’s important to note that short-term trading in the stock market, including with ETFs, is inherently risky and may not be suitable for all investors. For long-term investors, both VOO and VFIAX can be suitable options, as they offer exposure to the long-term growth potential of the S&P 500 index. VFIAX’s focus on long-term investment and professional management may be attractive to those who prefer a more hands-off approach.
Risk Tolerance: The S&P 500 index can experience significant short-term volatility, and both VOO and VFIAX will reflect this volatility. Investors with a higher risk tolerance may be more comfortable with the potential short-term fluctuations and may choose to invest in either fund. However, investors with a lower risk tolerance may want to consider diversifying their portfolios further by including other asset classes, such as bonds or international stocks, in addition to their investment in VOO or VFIAX.
Investment Amount and Frequency: If an investor has a relatively small amount of money to invest and wants to start with a lower minimum investment, VFIAX’s Admiral Shares may be a better option. Additionally, if an investor plans to make regular contributions to their investment, the ability to set up automatic contributions with a mutual fund like VFIAX may be convenient. On the other hand, if an investor has a larger amount of money to invest and wants the flexibility to trade throughout the day, VOO may be a more suitable choice.
Conclusion
In conclusion, both the Vanguard S&P 500 ETF (VOO) and the Vanguard 500 Index Fund Admiral Shares (VFIAX) offer investors exposure to the S&P 500 index, which has a long history of providing returns and diversification. The choice between the two depends on various factors, including the investor’s investment horizon, risk tolerance, investment amount, and trading preferences.
For investors who value liquidity, intraday trading capabilities, and potentially slightly lower costs, VOO may be a suitable option. On the other hand, those who prefer a more traditional mutual fund structure, professional management, and the convenience of automatic contributions with a lower minimum investment may find VFIAX more appealing.
Regardless of which option is chosen, it’s important for investors to have a long-term perspective and to understand that investing in the stock market, including through index funds or ETFs, carries risks. Regular monitoring and periodic rebalancing of the investment portfolio can also help investors stay on track to meet their financial goals. By carefully considering their individual circumstances and conducting thorough research, investors can make an informed decision about whether to invest in VOO or VFIAX and build a portfolio that aligns with their investment objectives.
Related topics:
How Do No Load Funds Make Money
Is Vanguard Wellington Fund a Good Investment