In the complex world of financial planning and investment, various products and strategies cater to different needs and objectives. One such product that has gained attention in recent years is the viatical settlement contract. This article aims to provide an in-depth understanding of viatical settlements, explaining what they are, how they work, their benefits and risks, and the legal and regulatory framework surrounding them.
See Also: 10 Reasons Why You Should Consider Buying Life Insurance
What is a Viatical Settlement Contract?
A viatical settlement contract is a financial arrangement in which a person with a life-threatening illness sells their life insurance policy to a third party for a lump sum cash payment. The payment is typically less than the policy’s face value but more than the cash surrender value. The buyer, or the investor, then becomes the new beneficiary of the policy and assumes responsibility for paying the remaining premiums. When the insured person passes away, the investor receives the death benefit.
History and Evolution
The concept of viatical settlements emerged in the 1980s during the AIDS epidemic. At that time, many patients faced high medical costs and a limited life expectancy. Viatical settlements offered them a way to access immediate funds by selling their life insurance policies. Over the years, the viatical settlement market has evolved, and while it is not as prominent as it once was, it remains a viable option for those in need of liquidity.
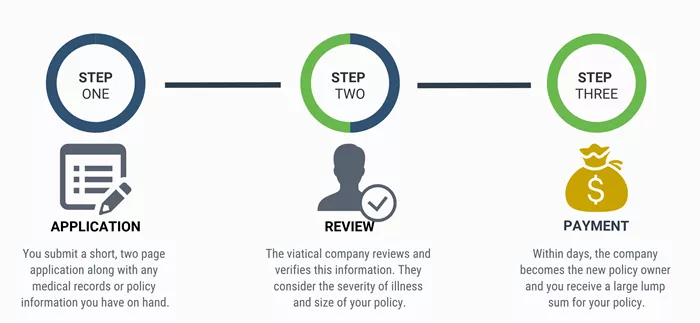
How Do Viatical Settlements Work?
To understand viatical settlements fully, it’s essential to grasp the mechanics of how they operate.
- Identification of the Insured: The process begins with identifying an individual, referred to as the viator, who has a life-threatening illness. The viator must have a life insurance policy with a significant death benefit.
- Policy Valuation: Next, the policy is evaluated. The value of the policy is determined based on factors such as the death benefit, the premiums required to keep the policy active, and the viator’s life expectancy.
- Offer and Negotiation: After valuation, potential buyers, usually institutional investors, make an offer to the viator. This offer is typically a percentage of the policy’s face value and is negotiated between the parties.
- Sale and Transfer: Once an agreement is reached, the policy ownership is transferred to the buyer. The buyer pays the agreed lump sum to the viator and assumes the responsibility for future premium payments.
- Receipt of Death Benefit: Upon the death of the insured, the buyer receives the full death benefit from the insurance company.
Benefits of Viatical Settlements
Viatical settlements offer several advantages for the insured and the investors.
- Immediate Cash for the Insured: The most significant benefit for the insured is the immediate access to cash. This can be crucial for covering medical expenses, improving the quality of life, or fulfilling other financial needs.
- Better Financial Planning: By liquidating their life insurance policy, viators can better plan for their remaining time, ensuring they have the resources needed for themselves and their families.
- Investment Opportunities for Buyers: For investors, viatical settlements present a unique investment opportunity. They can purchase policies at a discount and potentially receive a substantial return when the death benefit is paid out.
- Portfolio Diversification: Viatical settlements can provide diversification for investment portfolios, as they are not directly correlated with traditional financial markets.
Risks and Considerations
While viatical settlements offer benefits, they also come with significant risks and considerations.
- Life Expectancy Risk: One of the primary risks for investors is the uncertainty of the viator’s life expectancy. If the insured lives longer than expected, the investor may have to pay more in premiums, reducing the overall return on investment.
- Regulatory and Legal Risks: The viatical settlement market is subject to regulatory scrutiny. Laws and regulations can vary significantly by jurisdiction, and changes in these regulations can impact the viability and profitability of viatical settlements.
- Ethical Considerations: There are ethical concerns surrounding viatical settlements, primarily related to the exploitation of vulnerable individuals. It is crucial for all parties involved to adhere to ethical standards and ensure that the viator’s best interests are considered.
- Liquidity Risk: For investors, viatical settlements are relatively illiquid investments. Selling a policy before the insured’s death can be challenging, potentially locking up capital for an extended period.
- Tax Implications: Both viators and investors must be aware of the tax implications associated with viatical settlements. The lump-sum payment received by the viator may be subject to taxes, and the death benefit received by the investor could also have tax consequences.
Legal and Regulatory Framework
The viatical settlement industry is regulated to protect consumers and ensure fair practices. The regulatory framework can vary by country and state but generally includes the following elements:
- Licensing Requirements: Companies and individuals involved in viatical settlements must often be licensed by relevant regulatory authorities. This ensures that they meet specific standards and adhere to ethical practices.
- Disclosure Requirements: Regulations typically require full disclosure to the viator regarding the terms of the settlement, including the amount to be paid, the policy’s face value, and any fees or commissions involved.
- Consumer Protection Laws: Various consumer protection laws are in place to prevent fraud and exploitation. These laws are designed to ensure that viators receive fair value for their policies and that their rights are protected throughout the process.
- Tax Regulations: Tax laws applicable to viatical settlements can be complex. It is essential for both viators and investors to understand the tax implications of their transactions and seek professional advice if needed.
Market Participants
The viatical settlement market involves several key participants:
- Viators: These are the individuals with life-threatening illnesses who sell their life insurance policies. Viators typically seek viatical settlements to access immediate cash for medical expenses or other needs.
- Investors: Investors purchase the life insurance policies from viators. They can be institutional investors, such as hedge funds or private equity firms, or individual investors looking for alternative investment opportunities.
- Brokers: Brokers facilitate viatical settlements by connecting viators with potential investors. They play a crucial role in the negotiation and transaction process, often charging a commission for their services.
- Insurance Companies: Insurance companies are the entities that issue the life insurance policies. While they are not directly involved in the viatical settlement process, they are responsible for paying the death benefits to the new policyholders (the investors).
Case Study: A Practical Example
To illustrate how a viatical settlement works in practice, consider the following case study:
John is a 55-year-old man diagnosed with a terminal illness. He has a life insurance policy with a face value of $500,000. Facing high medical costs and wanting to ensure financial stability for his family, John considers selling his policy through a viatical settlement.
After consulting with a broker, John receives an offer of $250,000 from an institutional investor. The investor agrees to take over the premium payments and receive the $500,000 death benefit upon John’s death.
John accepts the offer, and the ownership of the policy is transferred to the investor. John receives the $250,000 lump sum, which he uses to cover his medical expenses and support his family. Upon John’s passing, the investor receives the $500,000 death benefit, resulting in a profit.
Ethical Considerations and Best Practices
Given the sensitive nature of viatical settlements, ethical considerations are paramount. Both viators and investors must adhere to best practices to ensure fair and ethical transactions.
- Transparency: Full transparency is crucial in viatical settlements. Viators should be fully informed of all aspects of the transaction, including the financial implications and any fees involved.
- Fair Valuation: Policies should be fairly valued to ensure that viators receive a reasonable payout. Investors should not take advantage of the viator’s vulnerable position.
- Confidentiality: The privacy of the viator should be respected throughout the process. Personal and medical information should be kept confidential and only disclosed when necessary and with the viator’s consent.
- Regulatory Compliance: All parties involved must comply with relevant laws and regulations. This includes obtaining the necessary licenses and adhering to consumer protection laws.
- Ethical Conduct: Ethical conduct should guide all interactions. This includes treating the viator with respect, honesty, and compassion.
Future of Viatical Settlements
The future of viatical settlements is influenced by various factors, including medical advancements, regulatory changes, and market conditions.
- Medical Advancements: As medical technology advances, the prognosis for many life-threatening illnesses improves. This could impact the viatical settlement market by reducing the number of eligible viators and altering life expectancy estimates.
- Regulatory Changes: Changes in regulations can have a significant impact on the viatical settlement market. Stricter regulations may increase compliance costs and reduce the attractiveness of viatical settlements for investors. Conversely, regulatory clarity and consumer protections could enhance market confidence.
- Market Conditions: The overall economic environment and market conditions play a role in the viatical settlement market. Economic downturns or changes in interest rates can affect investor appetite for viatical settlements and the availability of capital.
- Innovation: Innovation in financial products and services could lead to new opportunities and challenges in the viatical settlement market. For example, advancements in technology and data analytics could improve the accuracy of life expectancy estimates and streamline the transaction process.
Conclusion
Viatical settlement contracts provide a unique financial solution for individuals with life-threatening illnesses who need immediate access to cash. While they offer several benefits, including liquidity and financial planning opportunities, they also come with risks and ethical considerations. Understanding the mechanics, benefits, risks, and regulatory framework of viatical settlements is crucial for both viators and investors. By adhering to best practices and ethical standards, all parties involved can ensure fair and transparent transactions. As the market evolves, staying informed about medical, regulatory, and market developments will be essential for navigating the future of viatical settlements.