Stock trading can be an exciting and rewarding endeavor, but it’s essential to approach it with the right knowledge and strategy. Whether you’re looking to trade stocks as a hobby or aim to build a significant investment portfolio, starting the process with a clear plan will make all the difference. This guide will walk you through the necessary steps to begin trading and help you build a strong foundation for success in the stock market.
Step 1: Understand the Basics of Stock Trading
Before diving into trading, it’s important to grasp the basics. Stock trading involves buying and selling shares of publicly traded companies. When you buy stocks, you essentially own a small part of the company. The goal is to purchase shares at a low price and sell them at a higher price, profiting from the price difference. However, stock prices fluctuate based on various factors such as company performance, market trends, and economic conditions.
Key Terms to Know:
-
Shares: A unit of ownership in a company.
-
Stock Exchange: A marketplace where stocks are bought and sold (e.g., the New York Stock Exchange or Nasdaq).
-
Broker: A professional who helps facilitate stock trades on your behalf.
-
Dividend: A portion of a company’s profits paid to shareholders.
-
Bull Market: A market in which stock prices are rising.
-
Bear Market: A market in which stock prices are falling.
Understanding these basic terms will help you navigate the world of stock trading with confidence.
Step 2: Choose the Right Type of Trading
There are several types of trading strategies you can pursue. Some of the most common include:
-
Day Trading: This involves buying and selling stocks within the same day. Day traders capitalize on short-term price movements and need to closely monitor the market throughout the day.
-
Swing Trading: Swing traders hold stocks for several days or weeks to take advantage of price “swings” or trends. This type of trading requires less time than day trading but still requires significant market analysis.
-
Position Trading: Position traders take a longer-term approach, holding stocks for months or years. This strategy is less time-intensive but requires careful research and patience.
Choose the type of trading that suits your lifestyle, risk tolerance, and time commitment.
Step 3: Open a Trading Account
To trade stocks, you need to open a trading account with a brokerage. This account will allow you to buy and sell stocks. Here’s how to choose the right brokerage:
-
Commissions and Fees: Look for a brokerage with low commissions and fees. Some brokerages offer commission-free trades, while others charge a fee per transaction.
-
User Interface: Choose a brokerage with an easy-to-use platform. A simple and intuitive interface will make your trading experience more manageable.
-
Research Tools: Some brokerages offer advanced research tools, stock analysis, and educational resources to help you make informed decisions.
-
Customer Support: Ensure the brokerage provides reliable customer support to assist with any questions or technical issues.
Some popular brokerages for beginners include Robinhood, E*TRADE, TD Ameritrade, and Fidelity.
Step 4: Learn How to Analyze Stocks
To make informed decisions when buying and selling stocks, you must learn how to analyze them. Stock analysis can be broken into two main types:
Fundamental Analysis:
This involves evaluating a company’s financial health by looking at its earnings, revenue, debt, and other key financial indicators. Key metrics include:
-
Earnings Per Share (EPS): A measure of a company’s profitability.
-
Price-to-Earnings (P/E) Ratio: The ratio of a company’s current share price to its earnings per share.
-
Return on Equity (ROE): A measure of a company’s profitability relative to shareholders’ equity.
Technical Analysis:
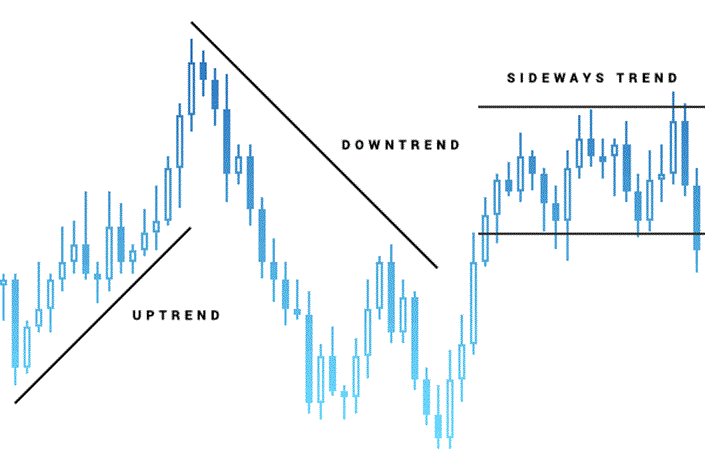
This focuses on studying price charts and using patterns, trends, and other indicators to predict future price movements. Some popular technical indicators include:
-
Moving Averages: The average price of a stock over a specific time period.
-
RSI (Relative Strength Index): A momentum oscillator that helps identify overbought or oversold conditions.
-
Support and Resistance Levels: Price levels where a stock tends to reverse direction.
Many traders combine both fundamental and technical analysis to make decisions.
Step 5: Develop a Trading Strategy
Having a clear strategy is crucial for success. A good strategy should align with your goals, risk tolerance, and available time. Here are some tips for developing your strategy:
-
Set Clear Goals: Determine what you want to achieve with trading (e.g., short-term profits, long-term investments, etc.).
-
Risk Management: Decide how much risk you’re willing to take on each trade. A common rule is to risk no more than 1-2% of your portfolio on a single trade.
-
Diversify: Don’t put all your money into one stock or sector. Spread your investments across different industries and asset classes to reduce risk.
-
Stay Disciplined: Stick to your strategy and avoid emotional trading. It’s easy to make impulsive decisions when the market is volatile, but sticking to your plan is key.
Step 6: Practice with a Demo Account
Many brokerages offer demo accounts that allow you to practice trading without using real money. These accounts simulate live market conditions, so you can get a feel for trading without the risk. Use the demo account to test your strategies and learn how to place orders, manage trades, and analyze market conditions.
Step 7: Start Trading with Real Money
Once you’re comfortable with your strategy and have practiced using a demo account, you can start trading with real money. Start small, especially if you’re new to the market. As you gain experience and confidence, you can gradually increase your investments.
Tips for Starting Small:
-
Start with a small amount of money that you’re willing to lose.
-
Avoid margin trading at first, as it involves borrowing money to trade and can lead to significant losses if the market moves against you.
-
Focus on a few stocks or sectors that you understand well.
Step 8: Monitor Your Trades and Learn from Mistakes
After making your first few trades, it’s important to monitor them regularly. Keep track of your gains and losses, and learn from both. Trading is a continuous learning process, and even the most successful traders experience setbacks. Keep refining your strategy and learning from your mistakes to improve your skills over time.
Step 9: Stay Updated with Market News
The stock market is influenced by various external factors, such as economic data, company news, and global events. Staying informed about these factors will help you anticipate market movements and make better trading decisions. Use news sources, financial websites, and reports from analysts to keep up to date with market trends.
Step 10: Review Your Progress and Adjust Your Strategy
As you gain more experience, take time to regularly review your trading progress. Assess your success rate, profitability, and any mistakes you’ve made. Based on your findings, adjust your trading strategy to improve your performance. Constant self-reflection is key to becoming a better trader.
Conclusion
Starting stock trading can seem overwhelming at first, but by following a structured approach, you can navigate the complexities of the market with confidence. Understanding the basics, choosing the right strategy, analyzing stocks, and managing risk are essential steps to becoming a successful trader. Remember to practice patience and discipline, and never stop learning. Stock trading is a journey that requires continuous effort, but with time and experience, it can become a powerful tool for building wealth.
Whether you’re trading for short-term profits or investing for the long haul, always stay informed, keep refining your strategy, and embrace the lessons that come with each trade. By doing so, you’ll improve your trading skills and increase your chances of success in the dynamic world of stock markets. Stay focused, and your persistence will pay off.
Related Topics: